MODULATOR VIDEO
Objectives:
1. 1. Measuring the frequency spectrum of video transmission.
2. 2. Determine the carrier frequency range image and sound carrier frequency.
3. 3. Specifies the field width (bandwidth) on video transmission.
4. 4. Specify the type of modulation on the picture and sound.
Equipment Used:
1 Modulator video (VCD / VTR / video sender).
1 RCA cable connector - BNC.
Circuit diagram:
Amplitude modulation or AM as it is often called, is a form of modulation used for radio transmissions for broadcasting and two way radio communication applications. Although one of the earliest used forms of modulation it is still in widespread use today.
The first amplitude modulated signal was transmitted in 1901 by a Canadian engineer named Reginald Fessenden. He took a continuous spark transmission and placed a carbon microphone in the antenna lead. The sound waves impacting on the microphone varied its resistance and in turn this varied the intensity of the transmission. Although very crude, signals were audible over a distance of a few hundred metres, although there was a rasping sound caused by the spark.
With the introduction of continuous sine wave signals, transmissions improved significantly, and AM soon became the standard for voice transmissions. Nowadays, amplitude modulation, AM is used for audio broadcasting on the long medium and short wave bands, and for two way radio communication at VHF for aircraft. However as there now are more efficient and convenient methods of modulating a signal, its use is declining, although it will still be very many years before it is no longer used.
What is amplitude modulation?
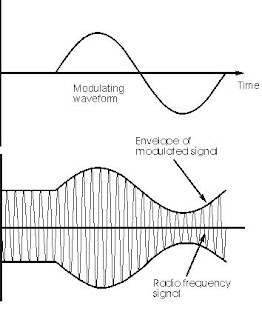
In order that a radio signal can carry audio or other information for broadcasting or for two way radio communication, it must be modulated or changed in some way. Although there are a number of ways in which a radio signal may be modulated, one of the easiest, and one of the first methods to be used was to change its amplitude in line with variations of the sound.
The basic concept surrounding what is amplitude modulation, AM, is quite straightforward. The amplitude of the signal is changed in line with the instantaneous intensity of the sound. In this way the radio frequency signal has a representation of the sound wave superimposed in it. In view of the way the basic signal "carries" the sound or modulation, the radio frequency signal is often termed the "carrier".
Amplitude Modulation, AM
When a carrier is modulated in any way, further signals are created that carry the actual modulation information. It is found that when a carrier is amplitude modulated, further signals are generated above and below the main carrier. To see how this happens, take the example of a carrier on a frequency of 1 MHz which is modulated by a steady tone of 1 kHz.
The process of modulating a carrier is exactly the same as mixing two signals together, and as a result both sum and difference frequencies are produced. Therefore when a tone of 1 kHz is mixed with a carrier of 1 MHz, a "sum" frequency is produced at 1 MHz + 1 kHz, and a difference frequency is produced at 1 MHz - 1 kHz, i.e. 1 kHz above and below the carrier.
If the steady state tones are replaced with audio like that encountered with speech of music, these comprise many different frequencies and an audio spectrum with frequencies over a band of frequencies is seen. When modulated onto the carrier, these spectra are seen above and below the carrier.
It can be seen that if the top frequency that is modulated onto the carrier is 6 kHz, then the top spectra will extend to 6 kHz above and below the signal. In other words the bandwidth occupied by the AM signal is twice the maximum frequency of the signal that is used to modulated the carrier, i.e. it is twice the bandwidth of the audio signal to be carried.
How to emit (transmit) signal is amplitude modulated image similar to a radio broadcasting system that has been known. In both cases, the amplitude of a carrier wave radio frequency (RF) is made varies with the modulating voltage. Modulation is a signal of fundamental frequency (baseband). On television, this baseband signal is a composite video signal. Broadcast television is really such a radio system, but includes pictures and sound. Sound signal emitted by joining in it frequency modulation (FM) on a separate carrier wave transmitter in the same channel as the image signal.
Understanding the image signal is used here to mean a modulated carrier wave. The video signal is a signal to a picture tube. Video signal to the television audio signal corresponds to the sound system. Details are clearer than the image signal AM (amplitude modulation picture) and an FM voice signal.
Figure 1 wave amplitude modulated composite video signal.
a. b.
Figure 2. a). Image signal AM frequency spectrum a). Without VSB. b). With VSB
Figure 2.a shows the frequency spectrum of video transmission that produces an image signal comprising AM picture carrier frequency (center frequency) and sound carrier frequencies (frequency side of the upper and lower side frequencies) - without VSB, while Figure 2b shows the frequency spectrum in transmission generate video image signals of AM frequencies only have the upper side only (with VSB).
Experimental Procedure:
- Calibration Spectrum Analyzer to determine the reference spectrum.
- Set-up instruments like in the picture above.
- ON the instrument.
- Measure the output video modulator (RF) using the Spectrum Analyzer and observe the frequency spectrum.
- Image of the frequency spectrum.
- Determine how much an image carrier frequency, carrier frequency sounds, and the difference frequency picture carrier and sound carrier frequency.
- Observe the spectrum, determine the type of modulation used in transmission, by way of changing the freq. SPAN (skala diperkecil). SPAN (reduced scale).
- Figure spktrum frequencies multiples of the base frequency.
Question:
- What system is used in the video modulator?
- From step 6, how to know what types of modulation?
Experimental results:
Ref = 105dBμ BW = 300 KHz CF = 206 MHz CP1ΔF - 29,6 MHz 10 MHz / DIV ΔV + 10.8 dB Picture Carrier Frequency: LSB = 206 MHz – 29,6 MHz= 176,4MHz USB = 206 MHz + 29,6 MHz=235,6MHz Voice carrier frequency: can not be seen because of the frequency spectrum analyzer with very small | |
Ref = 105dBμ BW = 300 KHz CF = 200 MHz CP1ΔF -10,0 MHz 10 MHz / DIV ΔV + 10.8 dB Picture Carrier Frequency: LSB = 200 MHz –(-6,8MHz)=206,8MHz USB = 200 MHz +(-6,8MHz)=193,2MHz Voice carrier frequency: can not be seen because of the frequency spectrum analyzer with very small. | |
Ref = 105dBμ BW = 1 MHz CF = 213 MHz CP1ΔF -148 MHz 50 MHz / DIV ΔV + 10 dB Picture Carrier Frequency: LSB = 213 MHz –(-148 MHz)= 361MHz USB = 213 MHz + (-148 MHz)= 65MHz Voice carrier frequency: can not be seen because of the frequency spectrum analyzer with very small. |
Data Analysis:
1. Viewed from the image spectrum that we get can we know that the value of experiment such as::
Carrier frequency: 206 MHz
CP1ΔF - 29,6 MHz
Then:
LSB = 206 MHz – 29,6 MHz= 176,4MHz
USB = 206 MHz + 29,6 MHz= 235,6 MHz
Carrier frequency: 206 MHz
CP1ΔF - 29,6 MHz
Then:
LSB = 206 MHz – 29,6 MHz= 176,4MHz
USB = 206 MHz + 29,6 MHz= 235,6 MHz
Voice carrier frequency: can not be seen because of the frequency spectrum analyzer with extremely small compared with the frequency carrier
2. For frequencies multiples:
Frequency of multiples of picture 1 in: 206 MHz
Frequency of multiples of picture 2 in: 200 MHz
Frequency of multiples of picture 1 in: 206 MHz
Frequency of multiples of picture 2 in: 200 MHz
Frequency of multiples of picture 3 in: 213 MHz
Answer Question:
- Modulation system used in the video are amplitude modulation, because the signal amplitude information affect the amplitude of the carrier signal, the signal information into the cover of the carrier signal. Image Signal modulated A common use of signal Am is: AM radio broadcasting is widely used for broadcast AM radio wave signal, the TV picture (Video), Radio communication: aircraft, amateur radio (SSB), CB radio (Citizens Band Radio). Digital data transmission: Modems Computers (combination with QAM modulation)Figure of Amplitude Modulation
- Known types of modulation are amplitude modulation can be seen from the changes in amplitude and has a spectrum of AM.
Based on the equation of the spectrum signal modulated AM. Amplitude modulation will have 3 (three frequencies):
• Fc : carrier frequency signal
• LSB: Lower Side Band frequency (LSB), namely the difference frequency carrier signal and the signal information.
• USB: Upper Side Band frequency (USB) is the number of carrier signal frequency and signal information.
Conclusion:
- In a video modulator that is used is amplitude modulation Modulation (AM)
- Amplitudo modulation is shown on a spectrum analyzer displays the three frequencies namely:
Ø Carrier Frequency
Ø Frequency of Lower Side Band (LSB), the difference frequency carrier signal and the signal information.
Ø Frequency of Upper Side Band (USB), the number of carrier signal frequency and signal information.
- The difference between USB and LSB frequencies are = 59,6 MHz
- Bandwidth in used in this experiment is 300 KHz bandwidth







Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar